[ad_1]
× shut
April 17, 2021, was a day like another day on the solar, till a superb flash erupted and an unlimited cloud of photo voltaic materials billowed away from our star. Such outbursts from the solar are usually not uncommon, however this one was unusually widespread, hurling high-speed protons and electrons at velocities nearing the pace of sunshine and putting a number of spacecraft throughout the interior photo voltaic system.
Actually, it was the primary time such high-speed protons and electrons—referred to as solar energetic particles (SEPs)—had been noticed by spacecraft at 5 completely different, well-separated places between the solar and Earth in addition to by spacecraft orbiting Mars. And now these various views on the photo voltaic storm are revealing that several types of doubtlessly harmful SEPs will be blasted into area by completely different photo voltaic phenomena and in numerous instructions, inflicting them to change into widespread.
“SEPs can hurt our expertise, reminiscent of satellites, and disrupt GPS,” stated Nina Dresing of the Division of Physics and Astronomy, College of Turku in Finland. “Additionally, people in area and even on airplanes on polar routes can endure dangerous radiation throughout robust SEP occasions.”
Scientists like Dresing are keen to seek out out the place these particles come from precisely—and what propels them to such excessive speeds—to raised discover ways to defend folks and expertise in hurt’s approach. Dresing led a crew of scientists that analyzed what sorts of particles struck every spacecraft and when. The crew published its ends in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
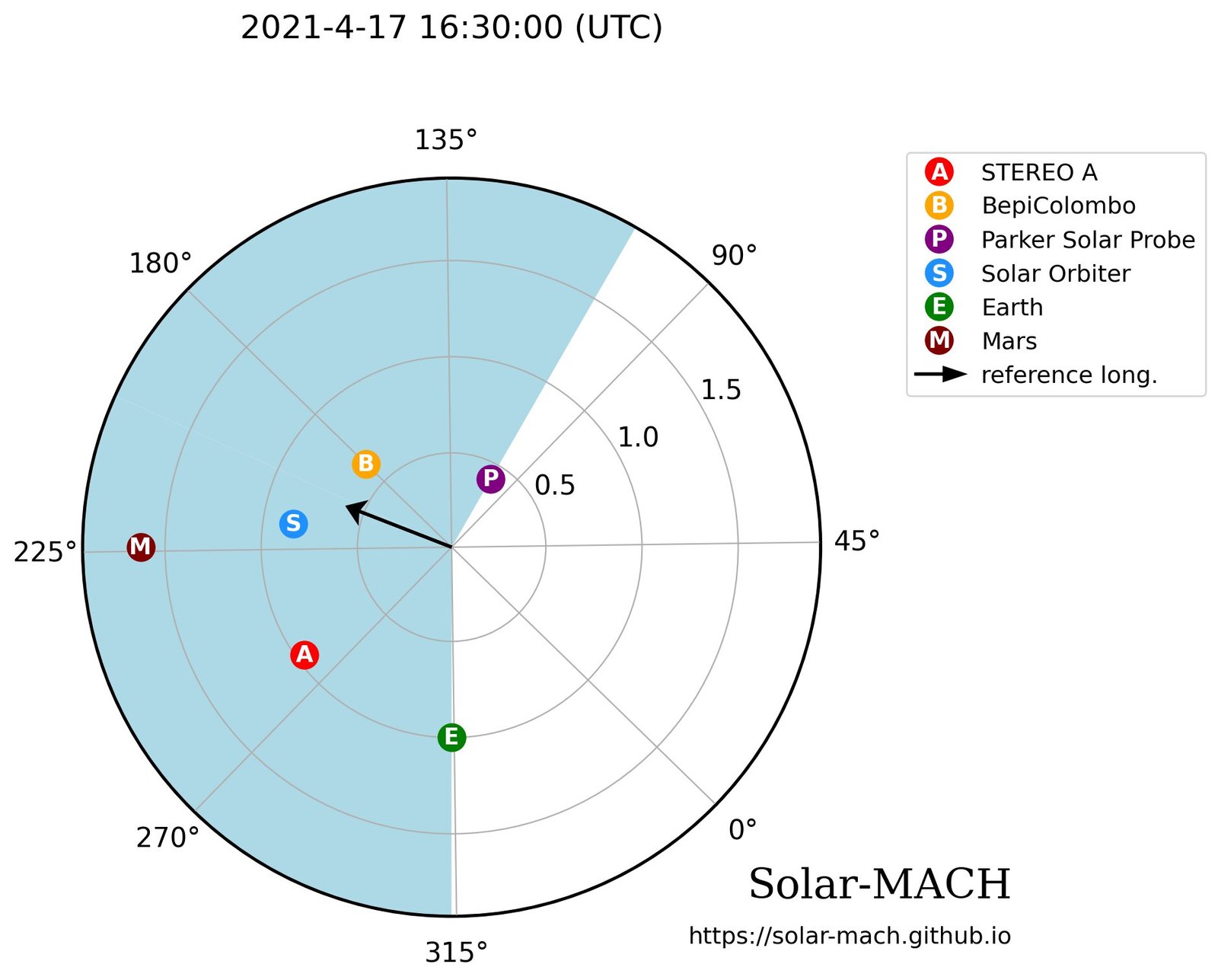
Presently on its method to Mercury, the BepiColombo spacecraft, a joint mission of ESA (the European Area Company) and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Company), was closest to the blast’s direct firing line and was pounded with essentially the most intense particles. On the identical time, NASA’s Parker Photo voltaic Probe and ESA’s Photo voltaic Orbiter had been on reverse sides of the flare, however Parker Photo voltaic Probe was nearer to the solar, so it took a tougher hit than Photo voltaic Orbiter did.
Subsequent in line was one in every of NASA’s two Photo voltaic Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) spacecraft, STEREO-A, adopted by the NASA/ESA Photo voltaic and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and NASA’s Wind spacecraft, which had been nearer to Earth and effectively away from the blast. Orbiting Mars, NASA’s MAVEN and ESA’s Mars Categorical spacecraft had been the final to sense particles from the occasion.
Altogether, the particles had been detected over 210 longitudinal levels of area (virtually two-thirds of the best way across the solar)—which is a a lot wider angle than sometimes coated by photo voltaic outbursts. Plus, every spacecraft recorded a special flood of electrons and protons at its location. The variations within the arrival and traits of the particles recorded by the assorted spacecraft helped the scientists piece collectively when and beneath what circumstances the SEPs had been ejected into area.
These clues steered to Dresing’s crew that the SEPs weren’t blasted out by a single supply suddenly however propelled in numerous instructions and at completely different occasions doubtlessly by several types of photo voltaic eruptions.
“A number of sources are seemingly contributing to this occasion, explaining its broad distribution,” stated crew member Georgia de Nolfo, a heliophysics analysis scientist at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland. “Additionally, it seems that, for this occasion, protons and electrons might come from completely different sources.”
The crew concluded that the electrons had been seemingly pushed into area rapidly by the preliminary flash of sunshine—a photo voltaic flare—whereas the protons had been pushed alongside extra slowly, seemingly by a shock wave from the cloud of photo voltaic materials, or coronal mass ejection.
“This isn’t the primary time that individuals have conjectured that electrons and protons have had completely different sources for his or her acceleration,” de Nolfo stated. “This measurement was distinctive in that the a number of views enabled scientists to separate the completely different processes higher, to verify that electrons and protons might originate from completely different processes.”
Along with the flare and coronal mass ejection, spacecraft recorded 4 teams of radio bursts from the solar in the course of the occasion, which may have been accompanied by 4 completely different particle blasts in numerous instructions. This commentary may assist clarify how the particles turned so widespread.
“We had completely different distinct particle injection episodes—which went into considerably completely different instructions—all contributing collectively to the widespread nature of the occasion,” Dressing stated.
“This occasion was in a position to present how necessary a number of views are in untangling the complexity of the occasion,” de Nolfo stated.
These outcomes present the promise of future NASA heliophysics missions that may use a number of spacecraft to review widespread phenomena, such because the Geospace Dynamics Constellation (GDC), SunRISE, PUNCH, and HelioSwarm. Whereas single spacecraft can reveal circumstances domestically, a number of spacecraft orbiting in numerous places present deeper scientific perception and supply a extra full image of what is occurring in area and round our residence planet.
It additionally previews the work that will likely be executed by future missions reminiscent of MUSE, IMAP, and ESCAPADE, which can examine explosive photo voltaic occasions and the acceleration of particles into the photo voltaic system.
Extra info:
N. Dresing et al, The 17 April 2021 widespread photo voltaic energetic particle occasion, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2023). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202345938