[ad_1]
A examine reveals the vital roles of dopamine and serotonin in decision-making primarily based on social context, exhibiting how these chemical compounds affect responses to provides in an ultimatum sport. This perception into neurotransmitter dynamics provides potential for brand spanking new remedies for Parkinson’s and psychiatric circumstances. Credit score: SciTechDaily.com
Worldwide staff decodes intricate dance of dopamine and serotonin in human brains, shedding gentle on social selections.
In a examine revealed in Nature Human Habits, scientists delve into the world of chemical neuromodulators within the human mind, particularly dopamine and serotonin, to disclose their position in social habits.
The analysis, performed in Parkinson’s illness sufferers present process mind surgical procedure whereas awake, homed in on the mind’s substantia nigra, an important space related to motor management and reward processing.
Led by Virginia Tech computational neuroscientist Learn Montague, the worldwide staff revealed a beforehand unknown neurochemical mechanism for a widely known human tendency to make selections primarily based on social context — persons are extra prone to settle for provides from computer systems whereas rejecting an identical provides from human gamers.
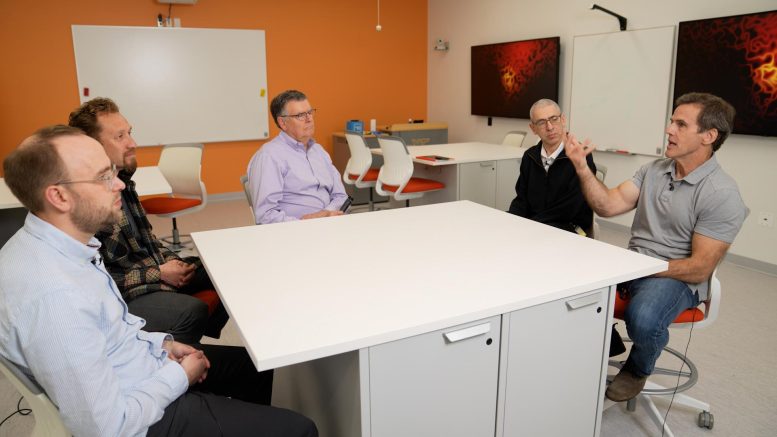

Scientists focus on their work to find insights into the complexities of the mind and thoughts. Lately, the researchers, together with (from left) Dan Bang of Aarhus College in Denmark, Ken Kishida of Wake Forest College College of Drugs, Michael Friedlander, government director of the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute; Peter Dayan, managing director of the Max Planck Institute for Organic Cybernetics in Tübingen, Germany, and Learn Montague, director of the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute Middle for Human Neuroscience Analysis, mirrored on achievements which have spanned a long time. Credit score: Clayton Metz/Virginia Tech
Perception From an Ultimatum Recreation
Within the examine, 4 sufferers receiving deep mind stimulation surgical procedure for Parkinson’s illness have been immersed within the “take it or depart it” ultimatum sport, a state of affairs the place they needed to settle for or reject various splits of $20 from each human and pc gamers. As an example, one participant could suggest to maintain $16, whereas the affected person will get the remaining $4. If the affected person rejects the cut up, then neither of them receives something.
“You may train folks what they need to do in these sorts of video games — they need to settle for even small rewards versus no reward in any respect,” mentioned Montague, the Virginia Tech Carilion Mountcastle professor with the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute at VTC and the senior writer of the examine. “When folks know they’re enjoying a pc, they play completely, identical to mathematical economists – they do what they need to do. However once they’re enjoying a human being, they can not assist themselves. They’re typically pushed to punish the smaller bid by rejecting it.”
Learn Montague, who led the analysis staff who recorded the chemical underpinnings of social decision-making, talks about relating essential parts of what makes us human beings. Credit score: Clayton Metz/Virginia Tech
Dopamine-Serotonin Dance
The concept folks make selections primarily based on social context just isn’t a brand new one in neural financial video games. However now, for the primary time, researchers present the impression of the social context could spring from the dynamic interactions of dopamine and serotonin.
When folks make selections, dopamine appears to intently observe and react as to if the present supply is best or worse than the earlier one, as if it have been a steady monitoring system. Serotonin, in the meantime, seems to focus solely on the present worth of the particular supply at hand, suggesting a extra case-by-case analysis.
This quick dance occurs towards a slower backdrop, the place dopamine is total greater when folks play different human beings – in different phrases, when equity comes into play. Collectively, these alerts contribute to our mind’s total evaluation of worth throughout social interactions.
“We’re shining a highlight on varied cognitive processes and at last receiving solutions to questions in finer organic element,” mentioned examine shared first writer Dan Bang, affiliate professor of scientific medication and Lundbeck Basis Fellow at Aarhus University in Denmark, and an adjunct affiliate professor on the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute.
“Dopamine ranges are greater when folks work together with one other human versus a pc,” Bang mentioned. “And right here it was necessary that we additionally measured serotonin to provide us confidence that the general response to social context is restricted to dopamine.”
Seth Batten, a analysis affiliate on the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute, constructed the electrodes used to report the dopamine-seratonin dance. Credit score: Clayton Metz/Virginia Tech
Seth Batten, a senior analysis affiliate in Montague’s lab and shared first writer of the examine, constructed the carbon-fiber electrodes that have been implanted in sufferers receiving Deep Mind Stimulation surgical procedure and helped gather the info on the Mount Sinai Well being System in New York.
“The distinctive twist with our technique is that it permits us to measure a couple of neurotransmitter at a time — the impression of that shouldn’t be misplaced,” Batten mentioned. “We’ve seen these signaling molecules earlier than, however that is the primary time we’ve seen them dance. Nobody has ever seen this dance of dopamine and serotonin in a social context earlier than.”
Teasing out the that means of the electrochemical alerts recorded from sufferers in surgical procedure was a serious problem that took years to unravel.
“The uncooked knowledge that we’re amassing from sufferers isn’t particular to dopamine, serotonin, or norepinephrine – it’s a combination of these,” mentioned Ken Kishida, a co-author of the examine and an affiliate professor of translational neuroscience, and neurosurgery, at Wake Forest College College of Drugs. “We’re basically utilizing machine-learning sort instruments to separate what’s within the uncooked knowledge, perceive the signature, and decode what’s occurring with dopamine and serotonin.”
Within the Nature Human Habits examine, researchers confirmed how the rise and fall of dopamine and serotonin are intertwined with human cognition and habits.
“Within the mannequin organism world, there’s a sweet retailer stuffed with fantastical methods to ask organic questions, but it surely’s more durable to ask questions on what makes you, you,” mentioned Montague, who can also be the director of the Middle for Human Neuroscience Analysis and the Human Neuroimaging Laboratory of the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute.
Addressing Parkinson’s
“In some unspecified time in the future, after we’ve evaluated sufficient folks, we’re going to have the ability to tackle the Parkinson’s illness pathology that’s given us this window of alternative,” mentioned Montague, who can also be a professor within the Virginia Tech School of Science.
In Parkinson’s illness, a major lack of dopamine-producing neurons within the brainstem is a key attribute that often coincides with the onset of signs.
This loss impacts the striatum, a mind area closely influenced by dopamine. As dopamine diminishes, serotonin terminals start to sprout, revealing a fancy interplay, as noticed in rodent fashions.
“Already there may be pre-clinical proof that the attrition of the dopamine system is telling the serotonin system, ‘Hey, we’ve bought to do one thing.’ However we’ve by no means been in a position to watch the dynamics,” Montague mentioned. “What we’re doing now is step one, however one would hope that when we stand up to a whole lot of sufferers, we’d be capable to relate this to symptomatology and make some scientific statements concerning the Parkinson’s pathology.”
In that respect, researchers mentioned a window is opening to study a variety of mind issues.
“The human mind is sort of a black field,” Kishida mentioned. “We now have developed another option to look inside and perceive how these programs work and the way they’ve develop into affected by varied scientific circumstances.”
Michael Friedlander, government director of the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute and a neuroscientist who was not concerned within the examine, mentioned, “This work is altering the whole subject of neuroscience and our capacity to question the human thoughts and mind — with a expertise that was simply not even imagined not a few years in the past.”
Psychiatry is an instance of a medical subject that would profit by this strategy, he mentioned.
“We now have an unlimited variety of folks on this planet that suffer from quite a lot of psychiatric circumstances, and, in lots of instances, the pharmacological options don’t work very properly,” mentioned Friedlander, who can also be Virginia Tech’s vp of well being sciences and expertise. “Dopamine, serotonin, and different neurotransmitters are in some methods intimately concerned with these issues. This effort provides actual precision and quantitation to grasp these issues. The one factor I feel we might be certain of is that this work goes to be extraordinarily necessary sooner or later for creating remedies.”
Extra Than a Decade within the Making
The hassle to measure neurotransmitters in real-time within the human mind started greater than 12 years in the past when Montague assembled a staff of specialists who “take into consideration considering, so much.”
In first-of-their-kind observations within the human mind the scientists revealed in Neuron in 2020, researchers revealed dopamine and serotonin are at work at sub-second speeds to form how folks understand the world and take motion primarily based on their notion.
Extra not too long ago, in a examine revealed in October within the journal Current Biology, the researchers used their technique of recording chemical adjustments in awake people to achieve perception into the mind’s noradrenaline system, which has been a longtime goal for drugs to deal with psychiatric issues.
And, in December within the journal Science Advances, the staff revealed that quick adjustments in dopamine ranges replicate a particular computation associated to how people study from rewards and punishments.
“We’ve made lively measurements of neurotransmitters a number of instances in several mind areas, and we’ve now reached the purpose the place we’re relating essential parts of what makes us human beings,” Montague mentioned.
Reference: “Dopamine and serotonin in human substantia nigra monitor social context and worth alerts throughout financial change” by Seth R. Batten, Dan Bang, Brian H. Kopell, Arianna N. Davis, Matthew Heflin, Qixiu Fu, Ofer Perl, Kimia Ziafat, Alice Hashemi, Ignacio Saez, Leonardo S. Barbosa, Thomas Twomey, Terry Lohrenz, Jason P. White, Peter Dayan, Alexander W. Charney, Martijn Figee, Helen S. Mayberg, Kenneth T. Kishida, Xiaosi Gu and P. Learn Montague, 26 February 2024, Nature Human Behaviour.
DOI: 10.1038/s41562-024-01831-w