[ad_1]
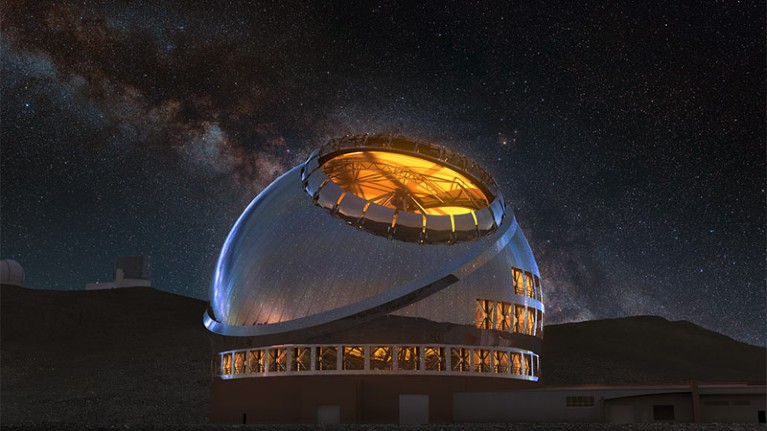

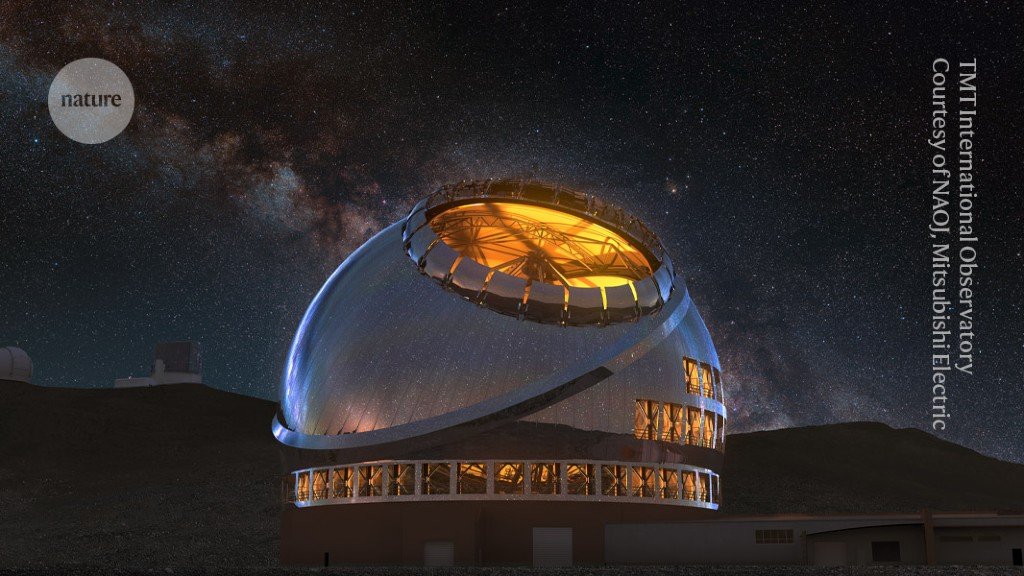
An artist rendering of the Thirty Meter Telescope, deliberate for development on Maunakea in Hawaii.Credit score: TMT Worldwide Observatory/Courtesy of NAOJ with the cooperation of Mitsubishi Electrical (CC BY 4.0)
US astronomers may need just one enormous ground-based telescope of their future, slightly than the 2 that many had hoped for.
They’ve been planning for years to construct the Large Magellan Telescope on a mountaintop in Chile, and the Thirty Meter Telescope on the Hawaiian mountain Maunakea. Building has began in Chile, whereas the Thirty Meter venture has been constructing telescope elements and doing different off-site work owing to concerns from Native Hawaiians over Maunakea, which they contemplate sacred. Each tasks are backed by worldwide teams of funders, however neither has the estimated US$3 billion wanted to totally fund its telescope.
Hawaii law could break years-long astronomy impasse
Many astronomers had hoped that the US Nationwide Science Basis (NSF) would contribute cash to cowl the funding shortfall. However final week the Nationwide Science Board, which oversees the NSF, beneficial that the company cap its giant-telescope contributions at $1.6 billion. The board additionally signalled that it was reluctant for the NSF to spend even that a lot, citing the necessity to construct different amenities “throughout a variety of science and engineering fields”.
Taken collectively, the board’s actions counsel that the NSF will most likely have to decide on which of the 2 telescopes to fund — there won’t be sufficient cash for each. The company is meant to attract up a plan by Might on methods to resolve which of the 2 to assist.
Each tasks might transfer forward in the event that they discover extra personal or different funding. However having the NSF concerned would make sure that US astronomers can be allotted a proportion of observing time on the telescopes, slightly than it being reserved for scientists who work with different funding companions. The US Congress might additionally allocate extra funds to the NSF for the telescopes, however many see that as unlikely on this time of tight budgets. US lawmakers nonetheless haven’t agreed on a funds for the present fiscal 12 months, and coverage watchers have predicted that science budgets will remain flat or even drop.
Falling behind
Looming over each telescope tasks is the truth that the European Southern Observatory is forward of them, rapidly constructing the 39-metre-wide Extraordinarily Giant Telescope in Chile.
To some US researchers, the concept of dropping entry to one of many two deliberate telescopes might signify a serious blow to US management in astronomy. “Nice imaginative and prescient ought to drive nice budgets, not vice versa,” says John O’Meara, chief scientist on the W. M. Keck Observatory in Kamuela, Hawaii.

The Large Magellan Telescope is meant to sit down atop a mountain in Chile’s Atacama Desert, as proven on this artist rendering.Credit score: Large Magellan Telescope – GMTO Company (CC BY 4.0)
To different scientists, the announcement is a long-needed push, on condition that it’s been six years for the reason that tasks joined forces to ask the NSF for funding. “That is extremely excellent news,” says Michael Turner, an astronomer on the College of Chicago in Illinois who penned an editorial in Science in November arguing that the NSF ought to fund simply one of many tasks. “It was going nowhere, and these two tasks had been withering on the vine.”
After the Nationwide Science Board publicly introduced the funding cap on 27 February, a spokesperson for the 2 tasks launched a joint assertion saying that they learn the board’s suggestions “with nice curiosity”. They famous that a 2021 survey of US astronomers’ priorities for the next decade ranked constructing the 2 big telescopes on the prime of the listing for ground-based astronomy. In recent times, representatives for the 2 telescopes have been pitching the tasks — as soon as bitter rivals — as a partnership of 1 northern and one southern observatory that would collectively examine a lot of the night time sky. Now they may need to compete for survival.
US astronomy’s 10-year plan is super-ambitious
Right now’s largest ground-based telescopes, such because the Keck telescopes on Maunakea, have mirrors within the vary of 8 to 10 metres huge that collect gentle from the night time sky. Going up in scale would allow huge leaps ahead in astronomical discovery of exoplanets, supermassive black holes, star formation and different celestial objects.
The Large Magellan Telescope is supposed to mix seven mirrors to type a light-gathering floor that’s 25 metres huge. The Thirty Meter Telescope is designed to make use of 492 hexagonal segments to create a mirror that, as its title suggests, is 30 metres throughout. The plan to construct atop Maunakea has been on maintain because the state of Hawaii stands up a new stewardship authority for the mountain, which contains extra Native Hawaiian illustration than prior to now.
“These big telescopes have gotten dearer than philanthropy can afford,” Turner says. “We have to construct an [extremely large telescope], and we have to get going.”