[ad_1]
Astronomers introduced on April 5 that they could have detected a collision between a neutron star and a light-weight thriller object — an object bigger than the biggest identified neutron star, however smaller than the smallest identified black hole. The discovering sheds gentle on objects that exist on this murky realm, which was lengthy regarded as empty however, in current instances, has revealed in any other case.
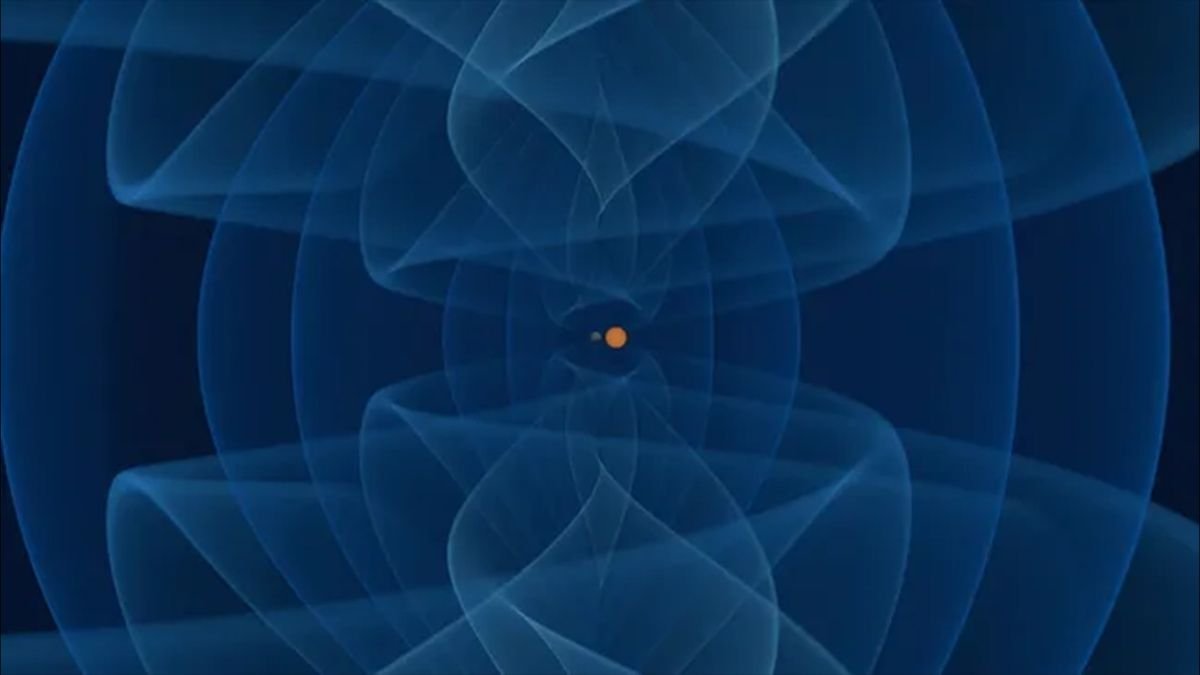
Extra particularly, a sign detected in a pocket of the universe roughly 650 million light-years from Earth signifies a uncommon merger between a neutron star and what astronomers suspect is a surprisingly light-weight black gap. The pair would have danced round each other and merged about 650 million years in the past, producing ripples within the material of house and time often called gravitational waves. These waves had been sensed and flagged on Might 29, 2023 by a community of antennas in Japan, Italy and the U.S. related to the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA (LVK) collaboration.
“These are uncommon occasions,” Evan Goetz, a LIGO researcher on the College of British Columbia (UBC) in Canada, informed Space.com. “It’s extremely thrilling for the neighborhood to check as the primary one in every of its sort.”
The black gap candidate, which is about 2.5 to 4.5 instances heavier than our solar, is heavier than the established restrict of two.5 suns for a neutron star — however lighter than the lightest identified black gap, which weighs about 5 photo voltaic lots. This locations the newfound object throughout the “mass hole,” a mysterious area that separates the heaviest neutron stars from the lightest black holes.
This discovery “hints at this ‘mass hole’ being much less empty than astronomers beforehand thought,” Michael Zevin, an astrophysicist on the Adler Planetarium, stated in a statement.
Associated: Uranus and Neptune aren’t made of what we thought, new study hints
Black holes, small and large, are born from the violent deaths of immensely large stars. A couple of fashions of how stars evolve, nevertheless, predict black holes with lots throughout the “mass hole” vary can not straight kind from such stellar deaths.
“It does seem that it might be attainable now with these observations,” Goetz stated. Maybe, he says, astronomers must tweak the fashions — or possibly “we actually do have a extra sophisticated evolution of a heavy neutron star that developed right into a black gap.”
“It is onerous to know simply from this one instance,” he stated.
In early 2020, astronomers introduced the primary conclusive detection of gravitational waves created by a collision which concerned a stellar remnant proper within the mass hole vary. Nonetheless, the invention workforce could not classify the thing with conviction on the time, concluding it might be both the largest identified neutron star or the smallest identified black gap.
As for the most recent discovering, astronomers say they can’t pinpoint simply the place within the sky the mammoth objects merged as a result of just one LVK detector was recording information when the sign was detected. However, the discovering has raised hopes that there could also be many extra such mass-gap objects on the market ready to be found.
“There may be much more doubtlessly we may discover and much more to look ahead to,” Heather Fong, a LIGO researcher at UBC, informed Space.com.
After a brief upkeep break, LVK detectors resumed measuring ripples in space-time on April 10. The LIGO workforce anticipates observing over 200 gravitational wave alerts by February 2025, together with hints of some objects throughout the elusive mass-gap vary.
The discovery was offered on the American Bodily Society assembly on Friday (April 5) and is awaiting peer evaluation.
Editor’s replace 4/11: That is the primary merger confirmed between a mass-gap object and a neutron star; mergers between black holes and neutron stars have been detected prior to now. This text has been up to date to mirror that.
Initially posted on Space.com.