[ad_1]
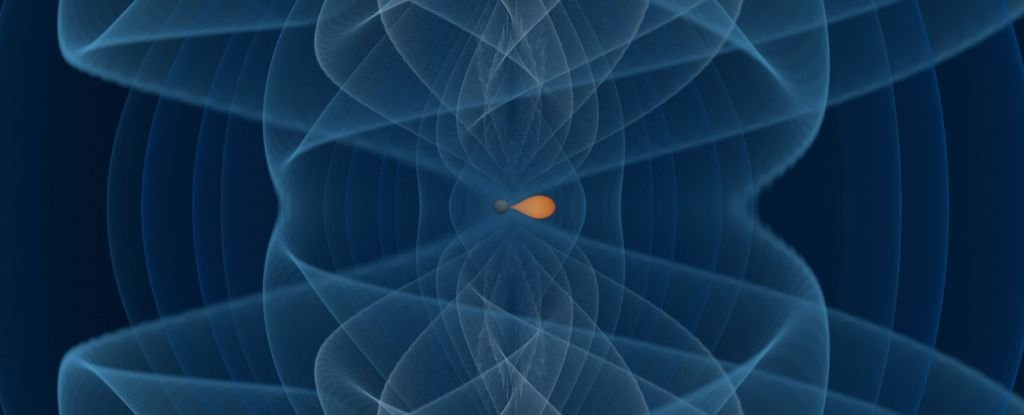
A gravitational wave detected in Could of final 12 months has given us a sort of cosmic collision we have by no means seen earlier than.
One of many plenty concerned was a neutron star. To date, so regular.
However we do not know what the opposite object was. That is as a result of it sits firmly in a distinct segment referred to as the decrease mass hole – the seemingly uncommon our bodies with plenty someplace between the chonkiest neutron stars and the titchiest black holes.
It is the primary time we have seen a gravitational wave occasion involving a neutron star and a mass hole object, and though we aren’t a lot nearer to realizing what the latter truly is, the invention excitingly means that these elusive thriller blobs may very well be frequent within the galaxy.
“Whereas earlier proof for mass-gap objects has been reported each in gravitational and electromagnetic waves, this method is very thrilling as a result of it is the primary gravitational-wave detection of a mass-gap object paired with a neutron star,” says astrophysicist Sylvia Biscoveanu of Northwestern College within the US.
“The remark of this method has necessary implications for each theories of binary evolution and electromagnetic counterparts to compact-object mergers.”
Neutron stars and stellar-mass black holes belong to the identical class of cosmic object. They’re what’s left of large stars which have reached the ends of their lives and gone supernova. The outer materials of the star explodes violently into house; however the core within the middle of the star – now not supported by the outward stress of fusion – collapses down into an ultradense object.
What determines the end result is mass. Stars with a beginning mass of about eight to 30 occasions the mass of the Solar find yourself as neutron stars. As soon as many of the stellar materials has been ejected, the collapsed core could have a mass of as much as 2.3 solar masses packed right into a sphere simply 20 kilometers (12 miles) throughout.
Stellar black holes type within the collapse of stars with way more mass, leaving highly-concentrated pockets of fabric that are likely to vary from round 5 to a dozen or so solar masses.
This is the place it will get attention-grabbing: we have detected very few objects between 2.3 and 5 photo voltaic plenty. And of these we have now detected, it is unclear whether we’re looking at a small black hole or a big neutron star.

Because the area between the heftiest neutron stars and lightest black holes is curiously devoid of detections, scientists consult with it because the decrease mass hole (to distinguish it from the black gap upper mass gap).
Gravitational wave detections are flying thick and fast these days, and astronomers are utilizing them to know black holes; their number and mass distribution offers us an concept of what number of there are on the market, and the way they type and develop.
The decrease mass hole is a thriller that scientists have been hoping gravitational waves would shed some gentle on. In 2020, the first detection came in of a merger between a black gap and a mass hole object, one thing that clocked in at 2.6 photo voltaic plenty.
The brand new detection, known as GW230529, was made in Could 2023. By analyzing the gravitational wave sign, the LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA collaborations had been in a position to decide that one of many objects concerned was between 1.2 and a pair of photo voltaic plenty. That is pretty solidly within the neutron star vary.
The second object, nevertheless, was between 2.5 and 4.5 photo voltaic plenty. That is firmly within the mass hole. The researchers imagine that it is in all probability a tiny black gap; there is no manner of realizing with the present knowledge, but it surely exceeds the theoretical upper limit for neutron star mass, so it is probably the most believable clarification right now.
However it’s the actual fact of the invention itself that’s most fun, and what it means for future detections.
“Earlier than we began observing the Universe in gravitational waves, the properties of compact objects like black holes and neutron stars had been not directly inferred from electromagnetic observations of programs in our Milky Approach,” says astrophysicist Michael Zevin of the Adler Planetarium within the US.
“The thought of a niche between neutron-star and black-hole plenty, an concept that has been round for 1 / 4 of a century, was pushed by such electromagnetic observations. GW230529 is an thrilling discovery as a result of it hints at this ‘mass hole’ being much less empty than astronomers beforehand thought, which has implications for the supernova explosions that type compact objects and for the potential gentle exhibits that ensue when a black gap rips aside a neutron star.”
The LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA gravitational wave detectors have all been present process upkeep, and up to date upgrades have dramatically improved detection sensitivity. The observing run is about to renew on 10 April 2024; we’re anticipating some extra juicy black gap discoveries within the close to future.
The analysis might be learn on the LIGO website.