[ad_1]
Fossilized bushes found by likelihood in southwest England belong to Earth’s earliest-known forest, new analysis has discovered. The 390 million-year-old fossils supplant the Gilboa fossil forest in New York state, which dates again 386 million years, because the world’s oldest recognized forest.
The brand new discovery highlights variations between the 2 ecosystems, suggesting forests went from being comparatively primitive to properly established over the course of just some million years, stated Neil Davies, the lead creator of a brand new research printed Feb. 23 within the Journal of the Geological Society.
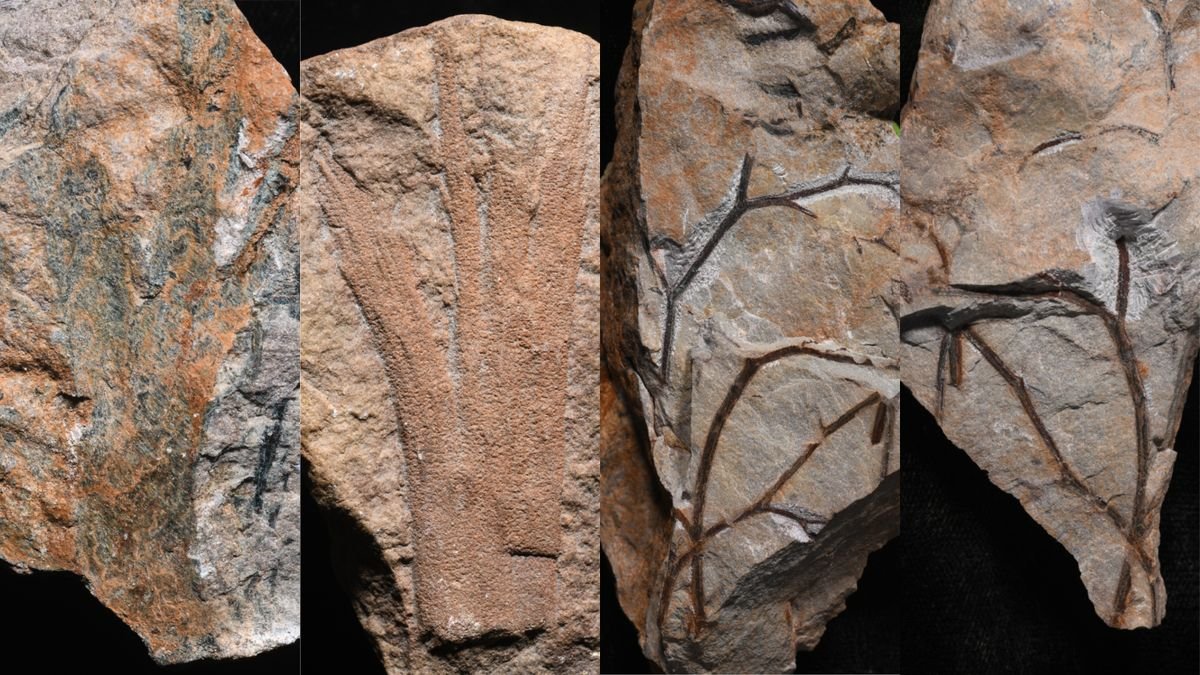
“Why it is necessary — broadly — is it ticks the containers of being the oldest fossil forest,” Davies, a professor within the Division of Earth Sciences on the College of Cambridge within the U.Ok., advised Dwell Science. The discovering can be exceptional as a result of it reveals stark variations between the complicated array of historical crops discovered at Gilboa and the newly found forest, which seems to have hosted only one kind of plant, Davies stated.
This now-extinct kind of crops, generally known as cladoxylopsids, is considered intently associated to ferns and sphenopsids (horsetails). “They seem like palm bushes, however they’re on no account associated to palm bushes,” Davies stated. “They have a protracted central stem and what seem like palm fronds coming off, however these palm fronds aren’t actually leaves — they’re really simply a number of twiglets.”
These twig-crowned bushes would have stood between round 6.5 and 13 toes (2 to 4 meters) excessive, which means “it would not have been a really tall forest,” Davies stated.
Associated: ‘Living fossil’ tree frozen in time for 66 million years being planted in secret locations
The fossil bushes had been preserved each as hole trunks full of sediment and as fallen logs that had been flattened over the eons — like “casts contained in the sediment,” Davies stated. Little scars the place branches used to connect to the bushes are nonetheless seen, he added.
Davies and his colleagues stumbled upon the forest remnants throughout fieldwork within the Hangman Sandstone Formation, which dates to the Center Devonian interval (393 million to 383 million years in the past). In the course of the Devonian period, what’s now the U.Ok. shaped a part of a continent known as Laurentia that sat just under the equator, which means the local weather was heat and dry, Davies stated.
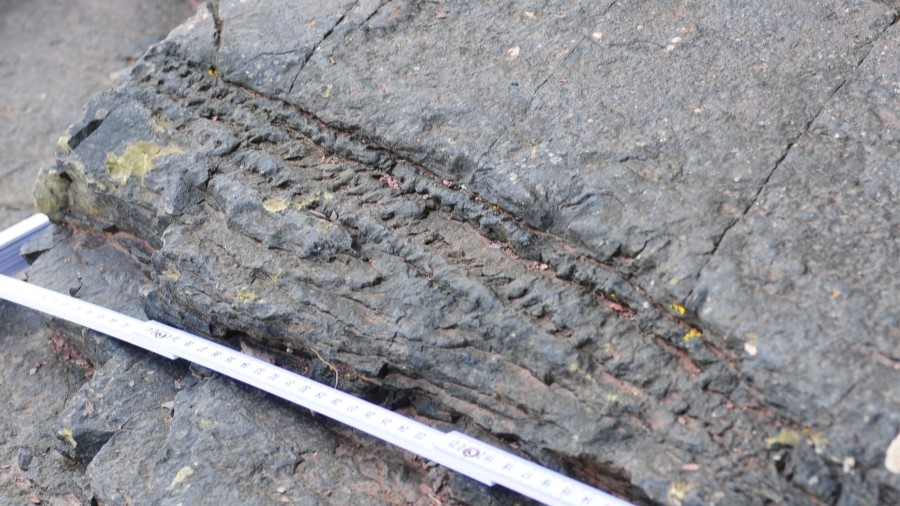

Older bushes exist elsewhere on this planet, with crops first colonizing land 500 million years ago, however this new discovery is the earliest instance of a forest with bushes rising shut collectively and en masse.
“We have discovered rocks the place you have bought standing bushes in development positions adjoining to one another over a set space,” Davies stated, “so we’re taking a look at a snapshot the place we are able to inform for particular that there have been bushes rising in that particular location and that the sediment we’re taking a look at is the forest flooring.”
Among the many fossil bushes, the researchers discovered trackways belonging to small Devonian critters. “Presently, there’s nothing a lot larger than a number of little arthropods knocking round on land,” Davies stated. “You would possibly discover some extra amphibian-type issues and fish in among the lakes and rivers close by.”
Whereas the researchers had initially got down to study sediments, the fortuitous discovery of fossil bushes could reveal a turning level in Devonian plant ecology. “It sort of means that round 390 million years in the past, there’s this sudden takeoff in forest-type environments,” Davies stated.