[ad_1]
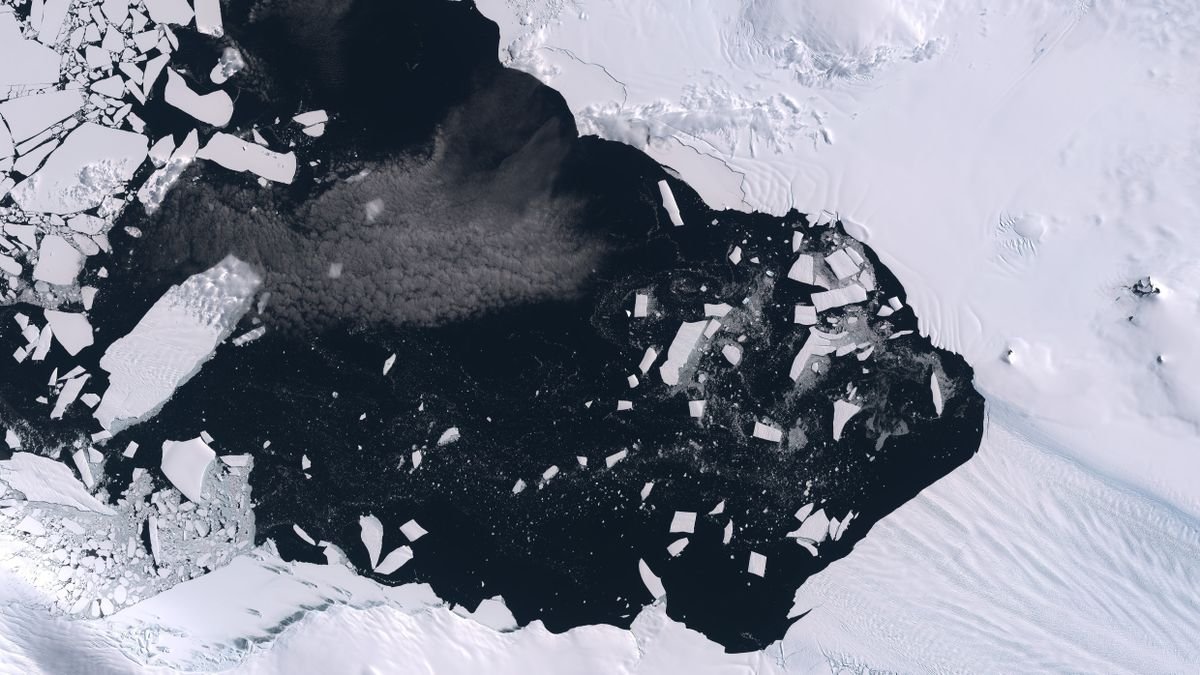
Scientists have noticed the quickest glacier fracture ever recorded — a crack in Antarctica’s ice that opened at roughly 80 mph (129 km/h).
The discovering reveals that enormous ice lots can shatter like glass, which might assist researchers higher perceive how local weather change will impression ice sheets.
“That is to our data the quickest rift-opening occasion that is ever been noticed,” Stephanie Olinger, lead writer of a brand new research into the glacier and a geophysicist at Stanford College, said in a statement. “This exhibits that beneath sure circumstances, an ice shelf can shatter. It tells us we have to look out for one of these conduct sooner or later, and it informs how we would go about describing these fractures in large-scale ice sheet fashions.”
The brand new research was printed Feb. 5 within the journal AGU Advances.
The 6.5-mile-long (10.5 kilometers) rift opened in 2012 on West Antarctica’s Pine Island Glacier, a key ice shelf that acts as a cork for the broader ice sheet, stopping it from sliding into the ocean.
Glaciologists outline rifts as cracks that move during a floating ice shelf and are sometimes seen as precursors to the calving of ice cabinets into the ocean.
To check the rift, the researchers mixed satellite tv for pc observations with seismic information taken from devices on the ice shelf.
At a cursory look, brittle ice is perhaps anticipated to shatter, however viscous seawater fills the cracks, which muddies the image. Within the new research, the scientists discovered that, not like larger ice sheets which can be breaking up slowly, the one at Pine Island is certainly shattering.
“Is rift formation extra like glass breaking or like Foolish Putty being pulled aside? That was the query,” Olinger mentioned. “Our calculations for this occasion present that it is much more like glass breaking.”The Pine Island Glacier and its southern neighbor, the Thwaites or “‘Doomsday”‘ Glacier, have been in retreat for the reason that Nineteen Forties and melting rapidly since the 1980s. Thwaites Glacier’s soften alone has contributed to a 4% rise in international sea ranges with the lack of roughly 595 billion tons (540 billion metric tons) of ice, and scientists imagine each glaciers could have already crossed key tipping factors for collapse.
The Pine Island Glacier has a floor space of roughly 62,660 sq. miles (162,300 sq. kilometers), and the Thwaites Glacier is of 74,130 sq. miles (192,000 sq. km). If the Thwaites Glacier have been to soften utterly, it could increase sea ranges by greater than 2 toes (0.6 meter). If this soften led to the broader destabilization of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, international sea ranges would rise by roughly 11 toes (3.4 m).
“Ice cabinets exert a very vital stabilizing affect on the remainder of the Antarctic ice sheet. If an ice shelf breaks up, the glacier ice behind actually hurries up,” Olinger mentioned. “This rifting course of is basically how Antarctic ice cabinets calve giant icebergs.”