[ad_1]
In accordance with a brand new mouse research, intestine micro organism might trigger imaginative and prescient loss in sure eye ailments, which might doubtlessly be handled with antibiotics.
Researchers from China and the UK found micro organism from the intestine in broken areas of the eyes of mice with mutations within the Crumbs homolog 1 (CRB1) gene, a significant reason for inherited eye ailments.
“We discovered an surprising hyperlink between the intestine and the attention, which is likely to be the reason for blindness in some sufferers,” says ophthalmologist Richard Lee from College School London, a senior writer of the research.
“Our findings might have enormous implications for reworking therapy for CRB1-associated eye ailments.”
It is early analysis, and we do not know if the identical mechanism occurs in people with the CRB1 mutation, which causes 4 % of retinitis pigmentosa, resulting in peripheral and evening imaginative and prescient loss, and 10 % of Leber congenital amaurosis, the place full blindness ensues in about a third of cases.
In CRB1-associated eye ailments, visible impairment begins younger. The retina – the tissue behind our eyes that converts wavelengths of sunshine into alerts that our mind interprets as imaginative and prescient – fails to develop its skinny layered construction of light-sensitive photoreceptor cells, changing into abnormally thick.
The group questioned if micro organism trigger retinal harm after their previous research discovered micro organism are unexpectedly frequent within the eyes.
Most of our trillions of gut bacteria are helpful quite than harmful and play a vital position in general well being. However Lee and colleagues assume the CRB1 mutation is letting intestine micro organism attain the eyes, the place they’ll contribute to imaginative and prescient loss.
The Crb1 protein encoded by the gene was regarded as solely discovered within the mind and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) – the outer blood-retina barrier that protects the attention. For the primary time, the researchers found that the intestinal wall additionally expresses the protein.
The Crb1 protein is important for sustaining a barrier between the intestine and the remainder of the physique, and the RPE. A mutated CBR1 gene would not specific sufficient of the Crb1 protein, resulting in breaches in these two protecting obstacles.
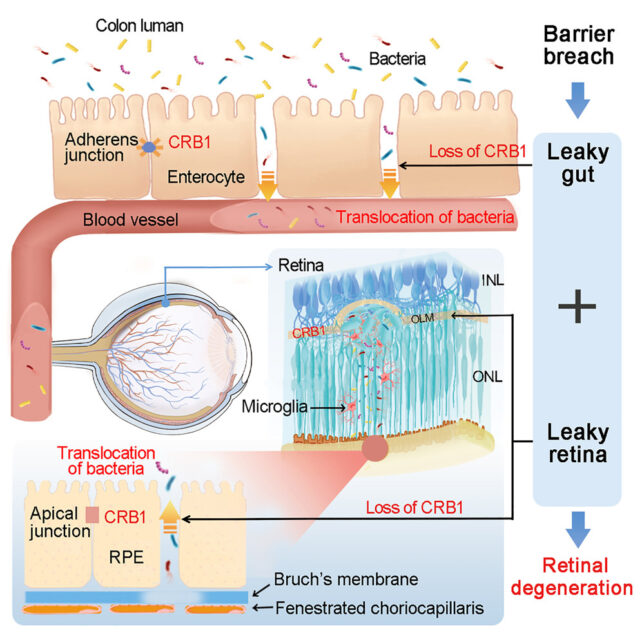
Mouse fashions of the mutation had impairments in each these obstacles, permitting intestine micro organism to go by way of the bloodstream into the retina and trigger lesions. Therapy with antibiotics lowered retinal harm and prevented imaginative and prescient loss.
When the researchers reintroduced regular Crb1 expression to the center of CRB1-mutated mice, it did not reverse the barrier breach, however harm to the retina was lowered. And CRB1-mutated mice with lowered bacterial populations did not present as a lot retinal harm both.
“We hope to proceed this analysis in scientific research to substantiate if this mechanism is certainly the reason for blindness in folks, and whether or not remedies focusing on micro organism might stop blindness,” says Lee.
This solely suggests a attainable hyperlink between eye ailments attributable to the CRB1 gene mutation. Nearly 100 genes affecting the retina’s light-sensitive photoreceptor cells could cause retinitis pigmentosa, and variants in at least 28 genes could cause Leber congenital amaurosis.
Gene remedy has shown promise in treating genetic eye diseases and has been a most important focus in creating remedies to date. Although in 2023, scientists linked particular immune cells migrating from the intestine to the retina to glaucoma severity.
The authors say their findings present that the intestine and the attention are linked in one other method – reside micro organism can transfer from a leaky intestine to the retina. We do not but absolutely perceive the intestine’s hyperlink to eye well being, however it may very well be one other therapy path to think about.
“As we have now revealed a wholly novel mechanism linking retinal degeneration to the intestine,” Lee says, “our findings might have implications for a broader spectrum of eye circumstances, which we hope to proceed to discover with additional research.”
The analysis has been revealed within the journal Cell.




